How Does the Brain Affect Behavior?
The brain serves as the control center of our body, playing a vital role in shaping our thoughts, feelings, and actions. From the simplest daily tasks to the most complex decisions, our brain influences everything we do.

So, how exactly does the brain impact our behavior? In this article, we’ll dive into the key ways the brain affects our actions, covering everything from emotions to memory and social interactions.
1. The Structure of the Brain and Its Impact on Behavior
The brain consists of several key regions, each responsible for different aspects of our behavior. To truly grasp how the brain influences our actions, it’s essential to understand its structure.
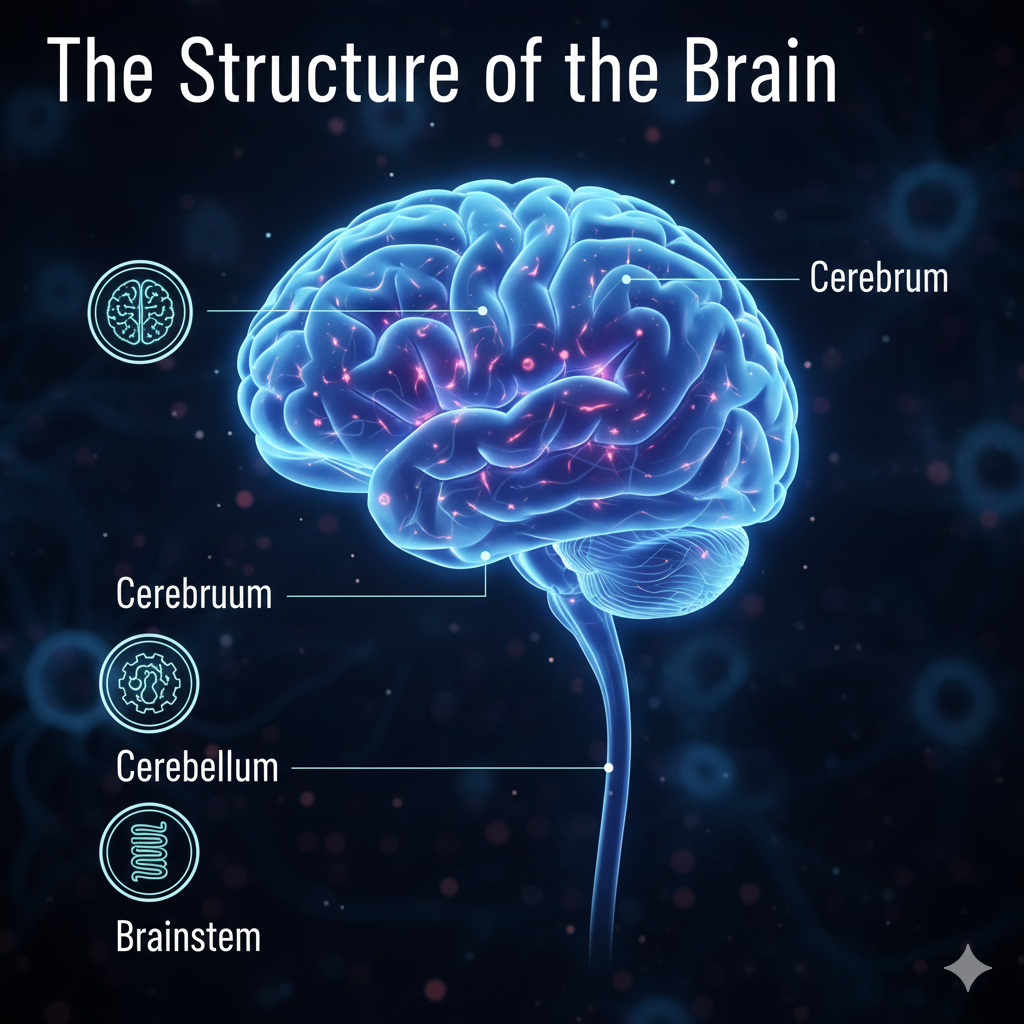
- Cerebrum: This is the largest part of the brain, overseeing higher-level functions like thinking, decision-making, and memory. The cerebrum is split into two hemispheres that collaborate to process information and guide our behavior.
- Cerebellum: Found at the back of the brain, the cerebellum is in charge of balance and coordination, helping us carry out motor activities like walking or picking up objects.
- Brainstem: This part of the brain manages basic life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and digestion. It regulates the automatic processes that are crucial for our survival.
All these regions work in harmony to guide our behavior, whether it’s through voluntary movements, thought processes, or automatic actions.
2. Neurotransmitters and Their Role in Behavior
Neurotransmitters are the brain’s chemical messengers that transmit signals between neurons. These chemicals have a significant impact on everything from our mood to our memory, and they can greatly influence our behavior. Let’s take a closer look at some important neurotransmitters:

- Dopamine: Often called the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, dopamine plays a key role in reward and pleasure. It affects motivation, decision-making, and even addiction.
- Serotonin: This neurotransmitter helps regulate mood, sleep, and appetite. Low levels of serotonin are frequently associated with conditions like depression and anxiety.
- Norepinephrine: This neurotransmitter plays a crucial role in managing our stress responses and boosting alertness. It’s a key player in the fight-or-flight reaction, gearing up our bodies to face potential threats.
- GABA: Known as the brain’s natural calming agent, GABA helps to ease excitability and anxiety, promoting a sense of relaxation and balance within the brain.
These neurotransmitters are essential for understanding how our brain influences our behavior. When there’s an imbalance in these chemicals, it can lead to shifts in mood, energy, and even the way we make decisions.
3. Emotions and the Brain’s Role in Behavior
Our emotions are regulated by the brain through various structures, particularly the limbic system. This system is key in processing emotions and memories, shaping our responses to different situations.

- Amygdala: The amygdala is crucial for processing feelings like fear and anger. It plays a significant role in the fight-or-flight response, prompting quick reactions to perceived dangers.
- Prefrontal Cortex: This area of the brain helps us manage our emotions by controlling impulsive behaviors and decision-making. It enables us to think before we act and helps us navigate our emotions in social contexts.
Together, the amygdala and prefrontal cortex influence how we express and regulate our emotions, which has a profound impact on our behavior. When this process falters, it can lead to emotional instability or impulsive actions.
4. Memory and Learning: How the Brain Shapes Future Behavior
Memory is another vital way the brain shapes our behavior. Our memories are stored in various brain regions, with the hippocampus playing a key role in forming and retrieving them.
- Memory Formation: The hippocampus is responsible for transforming short-term memories into long-term ones, allowing us to learn from our past experiences. These memories then guide our actions in similar situations down the line.
- Behavioral Conditioning: Our brains learn through a mix of rewards and punishments. When we experience positive outcomes, certain behaviors get reinforced, while negative outcomes can steer us away from others. This whole process, known as conditioning, plays a big role in shaping our actions over time.
The memories we create and the experiences we gather lay the groundwork for our behavior, guiding us to make informed choices based on what we’ve done in the past.
5. How the Brain Affects Social Behavior
Social behavior is closely tied to how our brains process information about those around us. The brain regions that handle social behavior help us navigate our interactions, grasp social norms, and make moral choices.
- Prefrontal Cortex: This area is crucial for making social decisions. It helps us understand the rules of social engagement and how our actions impact others.
- Mirror Neurons: These special neurons enable us to empathize with others by reflecting their emotions and actions. For instance, when we see someone smiling, our brains activate similar pathways, allowing us to feel that happiness too.
This connection sheds light on why we often mimic others’ behaviors and feel empathy in social settings. If there are disruptions in these brain areas, it can lead to challenges in social interactions, ultimately affecting our behavior.
6. Mental Health and the Brain’s Influence on Behavior
The structure and function of our brains are closely linked to our mental health. Conditions like depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia are associated with imbalances in neurotransmitters or abnormalities in certain brain regions, which can significantly influence our behavior.
- Depression: Low levels of serotonin and dopamine are often tied to depression, leading to behaviors such as withdrawal, disinterest in activities, and changes in sleep and appetite.
- Anxiety: When the amygdala is overactive, it can trigger excessive fear and anxiety. Those dealing with anxiety may find themselves experiencing heightened stress responses and engaging in avoidance behaviors.
- Schizophrenia:Schizophrenia is a complex disorder often linked to irregularities in dopamine levels, which can result in symptoms like hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking. Grasping the relationship between mental health and brain function is essential for tackling unusual behaviors and enhancing overall well-being.
7. Neuroplasticity: How the Brain Changes Over Time
One of the most intriguing features of the brain is its remarkable ability to change and adapt throughout our lives. This phenomenon, known as neuroplasticity, enables the brain to forge new connections in response to our experiences, learning, and even recovery from injuries.
- Learning and Behavior: Thanks to neuroplasticity, our behavior isn’t set in stone. With practice and dedication, we can refine our actions, reactions, and habits.
- Healing and Recovery: Neuroplasticity also plays a significant role in recovering from brain injuries. Sometimes, damaged areas of the brain can reorganize themselves, allowing other regions to take over the functions that were lost.
This adaptability highlights just how flexible and powerful our brains are in shaping and transforming our behavior over time.
Conclusion: How the Brain Affects Behavior
To wrap things up, the brain is crucial in shaping our behavior. It regulates our emotions, helps us form memories, and controls our social interactions, influencing every facet of how we act. By delving into the connection between the brain and behavior, we can gain insights into why we behave the way we do and how we can foster positive changes in our lives.
Whether it’s about enhancing emotional regulation, acquiring new skills, or managing mental health, the brain’s impact on our behavior is both profound and significant. Understanding this link can pave the way for better mental health and an improved sense of overall well-being.

